Understanding Surgery Retractors: Essential Tools for Surgical Success
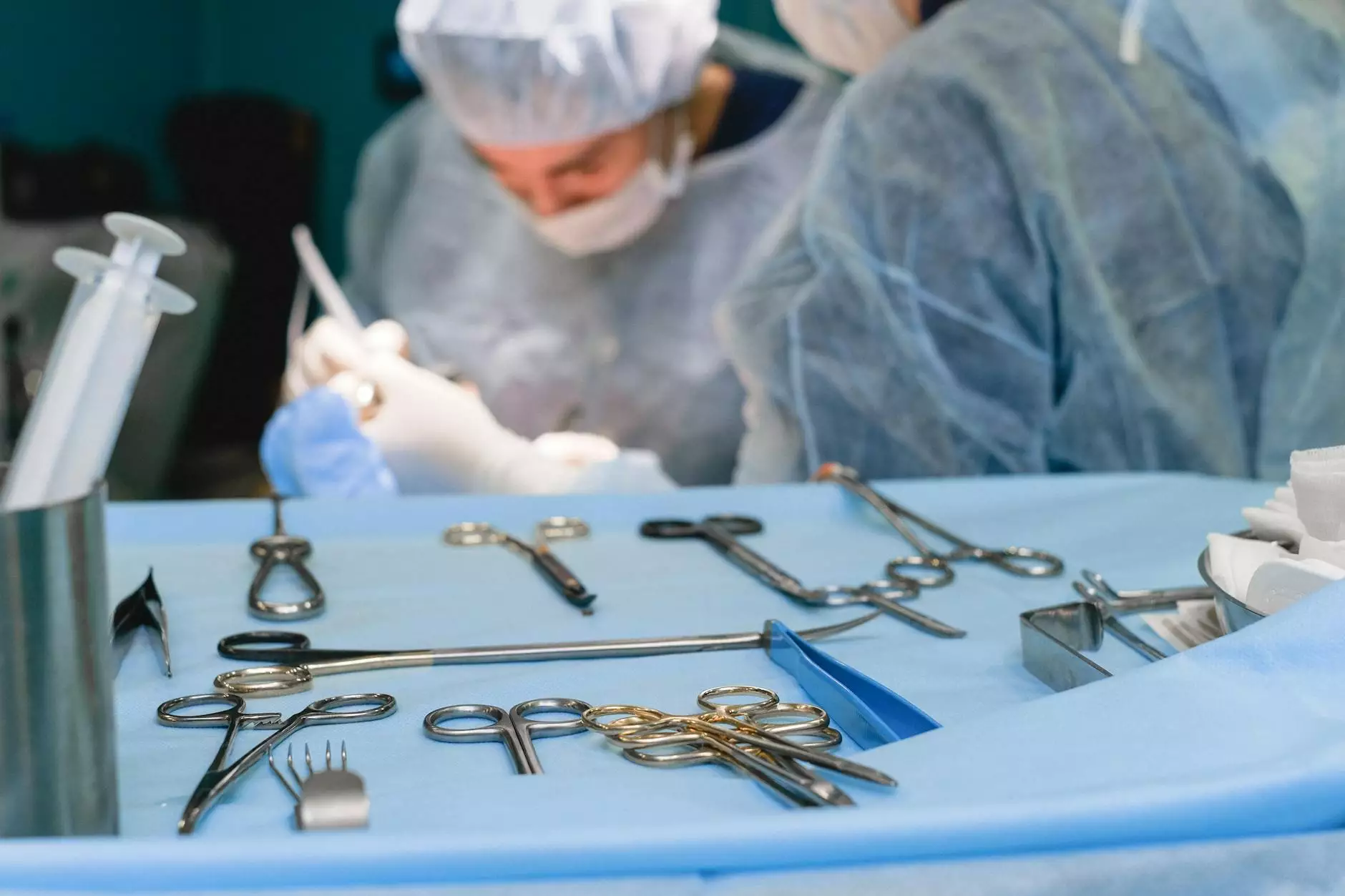
The field of medicine has witnessed remarkable advancements over the years, particularly in surgical procedures. Among the myriad of instruments utilized, surgery retractors stand out as pivotal tools that enhance the efficiency and precision of surgical operations. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the significance, types, applications, and proper handling of surgery retractors, while aligning with the key interests of health professionals and medical supplies providers.
The Significance of Surgery Retractors
Surgery retractors play a critical role in surgery by providing surgeons with a clear view and access to the surgical site. By holding back tissues, organs, and other structures, retractors significantly minimize obstruction, allowing for better identification of vital structures, improved surgical precision, and ultimately, enhanced patient outcomes. The correct use of surgery retractors can also expedite the surgical process, reducing time under anesthesia for patients.
Types of Surgery Retractors
There are various types of surgery retractors, each designed for specific procedures and anatomical areas. Below is a detailed overview of the major categories:
1. Handheld Retractors
Handheld retractors rely on the surgeon’s or assistant's hand during the procedure. They are designed to provide temporary retraction of the tissue. Examples include:
- Deavers Retractor: Commonly used in abdominal surgeries for holding back large sections of tissue.
- Richards Retractor: Known for its adjustable arms, utilized during intestinal and vaginal surgeries.
2. Self-Retaining Retractors
These retractors have mechanisms that allow them to hold tissues back on their own, alleviating the need for manual holding. This is particularly useful in lengthy procedures. Notable self-retaining retractors include:
- Balfour Retractor: Widely used in abdominal surgeries, providing excellent exposure while accommodating the bladder.
- Bookwalter Retractor: Adjustable and versatile, suitable for various major surgeries, including thoracic and abdominal.
3. Scissors Retractors
These tools integrate the functionality of scissors with retractors, allowing for simultaneous cutting and retraction. An example is:
- Parker Retractor: Utilized mainly in orthopedic surgeries, offering distinct advantages in accessing deep tissues.
Applications of Surgery Retractors
Surgery retractors have a wide range of applications across various surgical specialties. Here are some notable areas:
1. General Surgery
In general surgery, retractors are essential for exposing organs and tissues in procedures such as appendectomies, cholecystectomies, and other abdominal surgeries. Their ability to offer clear visibility significantly contributes to surgical success.
2. Orthopedic Surgery
In orthopedic surgeries, retractors provide crucial access to joints and bones. They help safely manipulate soft tissues around complex structures, ensuring the surgeon can operate effectively.
3. Neurosurgery
Neurosurgeons frequently use specialized retractors to navigate the intricate anatomy of the brain and spinal column. Precise retraction is imperative in preventing damage to surrounding neural tissues.
Choosing the Right Surgery Retractor
When selecting surgery retractors, several factors need consideration:
- Procedure Type: Different surgeries require specific retractors; understanding the procedure aids in choosing the correct instrument.
- Size and Shape: Retractors come in various sizes and shapes; ensure the selected tool fits the anatomy of the surgical site.
- Material: Stainless steel retractors are standard due to their durability and ease of sterilization.
Proper Handling and Maintenance of Surgery Retractors
The efficacy and longevity of surgery retractors depend significantly on their maintenance and proper handling. Here are several best practices:
1. Cleaning and Sterilization
Following usage, retractors must undergo thorough cleaning to remove blood, tissue, and contaminants. They should then be sterilized according to hospital protocols, typically involving steam autoclaving.
2. Inspection for Damage
Pre-and post-operative inspections are crucial for detecting any signs of wear or damage. Instruments showing corrosion, cracks, or deformities should be repaired or replaced immediately.
3. Proper Storage
After cleaning and sterilization, retractors should be stored in a designated area to prevent damage and ensure they are readily accessible for future use.
The Future of Surgery Retractors
As the medical field evolves, so do surgical instruments. Innovations in technology are paving the way for enhanced surgery retractors that integrate advanced materials and ergonomic designs to improve usability and performance. 3D printing technology is also being explored to create customizable retractors tailored to individual patient anatomies.
Conclusion
The importance of surgery retractors in the medical field cannot be overstated. Their ability to enhance visibility, improve surgical outcomes, and ultimately save lives makes them an indispensable tool in any surgical setting. With advancements in design and technology, the future holds promising enhancements that will continue to benefit both surgeons and patients alike. As medical professionals continue to explore and adopt these innovations, the reliability and effectiveness of surgical procedures will undoubtedly improve, reinforcing the vital role that retractors play in modern medicine.
Further Reading and Resources
For those interested in exploring more about surgery retractors and their applications, consider visiting the following resources:
- New Med Instruments - Your source for high-quality medical supplies.
- National Institutes of Health - Research on surgical techniques and tools.
- Medical Journal - Insights on advancements in surgical instruments.